The first issue of 2017 of Surface Innovations is available online. We open this first issue with two important contributions prepared by members of the External Advisory Board. In the first paper entitled “Contact Angles and Wettability: Towards Common and Accurate Terminology,” an international and interdisciplinary team of scientists led by Professor Abraham Marmur define terms describing contact angles, wettability, super-hydrophobicity and similar terminology. In the second contribution to this issue and entitled “Application of Thin-Layer Wicking Method for Surface Free Energy Determination,” Professor Emil Chibowski and his colleagues summarize theoretical fundamentals of the thin-layer wicking method and provide practical guidelines to this important experimental method used in wetting characterization of powder materials. They also offer directions on determination of solid surface free energy for powder material utilizing the experimental data produced with thin-layer wicking method. In the third contribution to this issue entitled “Unidirectional Droplet Motion on Crosswise-Striped Surface,” Gątarski and Nowicki analyze theoretically, using the Surface Evolver simulation program, behavior of liquid droplets on patterned heterogeneous surfaces made of parallel and alternating strips having different surface energies.
Coatings made of phospholipids are explored in surface chemistry and biomaterials laboratories to improve biocompatibility of metals commonly used in dental and orthopedic applications. In the fourth paper of this issue entitled “Model Study of Biostability of DPPC Layers Deposited by LB/LS on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy,” Yan et al. report on stability of monolayers and bilayers of 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, known as DPPC, deposited by the Langmuir-Blodgett/Langmuir-Schaffer (LB/LS) technique on titanium alloy biomaterial in aqueous phase (water, phosphate buffer saline, simulated body fluid and 1% Triton X-100 aqueous solution) at body temperature.
In the fifth paper of this issue entitled “Corrosion Behaviour of Microarc-Oxidised Magnesium Alloy in Earle’s Balanced Salt Solution,” Zhang et al. report their findings in corrosion behavior of a commercial AZ31 magnesium alloy, with a surface modified through microarc oxidation. And in the final paper of this issue “Modification of Silica-Alkyl Phase by Cationic Surfactant and Silica Precursor,” Sienkiewicz et al. demonstrate synthesis of novel sandwich-type of hybrid material using a sol-gel process.
We hope that the readers will find the content of this issue interesting and rewarding.
SI Volume 5 Issue 1
Point of Pride
One of our publications remains as the top cited paper for Surface Innovations in the last 3 years. The paper is entitled Guidelines to Measurements of Reproducible Contact Angles Using a Sessile-Drop Technique and was published at the end of 2013. Also second publication of ours entitled Physics and Applications of Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Surfaces and Coatings and published at the end of 2014 moved to the second place in citations for this journal in the last 3 years.
Full list of most cited publications for Surface Innovations is available online.
Publication on Zn-Li Alloys
Graduate student Shan Zhao led the project on formulation of new Zn-Li alloys for biomedical applications. In her first paper on Zn-Li alloys she reports a preparation of new Zn-xLi alloys (with x=2, 4, 6 at%). Structures of the formulated binary alloys were characterized by x-ray diffraction and optical microscopy. Mechanical testing showed that the incorporation of Li into Zn increased ultimate tensile strength from 560 MPa (x=6 at%). In vitro corrosion behavior was evaluated by immersion tests in simulated body fluid. The Zn-2Li and Zn-4Li corrosion study demonstrated that corrosion rates and products resemble those observed for pure Zn in vivo, and in addition, the Zn-4Li alloy exhibits higher resistance to corrosion as compared to Zn-2Li. The findings herein encourage further exploration of Zn-Li systems for structural use in biomedical vascular support applications with the ultimate goal of simplifying stent procedures thereby reducing stent related complications.
The findings are published in the Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A in the article entitled Structural Characteristics and In Vitro Biodegradation of a Novel Zn-Li Alloy Prepared by Induction Melting and Hot Rolling.
New Scholar from China
The SURFI Team welcomes a new addition to our team, Dr. Xubo Liu. Dr. Xubo Liu has arrived from the School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering at Nanchang University in P.R. China a few days before Christmas. Dr. Liu will help us to process and develop new zinc alloys during his one-year stay at Michigan Tech.
Season’s Greetings
I and Surface Innovations team would like to wish everyone happy holiday season and very successful 2017! Hope you will have chance to visit or interact with us next year.
SI Volume 4 Issue 4
The fourth issue of 2016 of Surface Innovations is available online. It contains four papers, starting with a review entitled “Superwettability integration: concepts, design and applications” by Moyuan Cao and Lei Jiang. This contribution offers a new and unique perspective on recent progress in design and application of complex integrated materials or integrated surface functionalities that produce uniquely premeditated surface wetting characteristics.
The penetration into and adhesion of a viscous binder to a porous solid matrix is an important problem within materials science and engineering, but has not received sufficient research attention in the past. In the article entitled “Evaluation of adhesion of asphalt binders using wicking experiments” by Artem Trofimov et al., the adhesion of an asphalt to a heterogeneous and porous rock is analyzed theoretically and experimentally.
Vijay Kumar Pal and his colleagues contribute to this issue with the technical report entitled “Hydrophobicity and tribology of large area textured Cu with nanogrown CuO.” The authors describe a method of fabricating copper surface with improved wear resistance and enhanced water repellency.
A briefing on slippery lubricant-infused porous surfaces and their application for anti-icing coatings was prepared by Yildrim Erbil and is entitled “Improvement of lubricant infused surfaces for anti-icing applications.” In this opinion, Dr. Erbil provides his perspective on technical and environmental challenges in formulation of anti-icing lubricant-based surfaces and coatings. He argues that water-based anti-freezing liquids should be favored in anti-icing applications since they have good ice accretion properties and environmental acceptance.
Successful Ph.D. Dissertation
Shan successfully defended her Ph.D. Dissertation entitled Structural characteristics and corrosion behavior of biodegradable Zn-Li alloys in stent application on December 19, 2016. She is scheduled to complete her entire Ph.D. program some time during the Spring 2017 semester.
Successful M.S. Defense
Avishan successfully defended her M.S. Thesis entitled Formulation and testing of biodegradable polymeric coating on zinc wires in cardiovascular stent application on December 14, 2016. She is scheduled to complete her entire M.S. program some time during the Spring 2017 semester.
Zinc and Inflammatory Cells
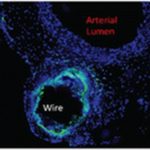
Although zinc and its alloys have many potential advantages, the inflammatory response has not been carefully examined in our research until recently. Using a modified wire implantation model, our close collaborators from Biomedical Engineering program led by Roger Guillory and Prof. Jeremy Goldman characterized the inflammatory response elicited by zinc and its alloys with aluminum. They found that inflammatory cells were able to penetrate the thick and porous corrosion layer that quickly formed around alloy implants. In contrast, a delayed entrance of inflammatory cells into the corrosion layer around pure zinc due to a significantly lower corrosion rate was associated with greater fibrous encapsulation, appearance of necrotic regions, and increased macrophage labeling. Interestingly, cell viability at the interface decreased among alloys with increasing alloying element, a trend associated with an increased CD68 and CD11b labeling and capsule thickness. Potentially, the shift to intergranular corrosion due to the aluminum addition increased the activity of macrophages. It was concluded that the ability of macrophages to penetrate and remain viable within the corrosion layer may be of fundamental importance for eliciting biocompatible inflammatory responses around corrodible metals. These findings were recently published in the article of the ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering journal and entitled “Corrosion characteristics dictate the long-term inflammatory profile of degradable zinc arterial implants.”
SI Volume 4 Issue 3
We are glad to share with you the content of the 3rd issue of 2016 of Surface Innovations, with six papers on bio-nano interfaces, which were selected and assembled by Prof. Candan Tamerler from the University of Kansas.