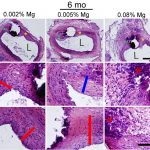
Biodegradable arterial implants based on zinc have been found to suppress neointimal hyperplasia, suggesting that biodegradable materials containing zinc may be used to construct vascular implants with a reduced rate of restenosis. However, the molecular mechanism has remained unclear. In this new report from Prof. Jeremy Goldman laboratories entitled Zn2+-Dependent Suppression of Vascular Smooth Muscle Intimal Hyperplasia from Biodegradable Zinc Implants, published in Materials Science and Engineering C, we show that zinc-containing materials can be used to prevent neointimal formation when implanted into the rat aorta. Indeed, neointimal cells were significantly more TUNEL positive and alpha-actin negative at the interface of biodegradable zinc vs. biostable platinum implants, in association with greater caspase-3 activity. Although zinc stimulated extensive neointimal smooth muscle cell (SMC) death, macrophage and proinflammatory markers CD68 and iNOS were not increased in neointimal tissue relative to biostable platinum control implants. Using arterial explants, ionic zinc was confirmed to promote SMC apoptosis by activating the caspase apoptotic signaling pathway. These observations suggest that zinc-containing materials can be used to construct vascular implants such as stents with reduced neointimal hyperplasia.
Functional materials/surfaces, bioabsorbable materials, and natural minerals
Formulation, separation, processing, characterization, and application
-
Recent Posts
Archives
- August 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- December 2021
- July 2021
- March 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- July 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- February 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- April 2014
- January 2014
- October 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
Categories