A new paper entitled A Simplified Analysis of the Effect of Nano-asperities on Particle-Bubble Interactions has been published in the Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing journal. This paper was invited by the editors and will be included in a special issue (first issue of 2018) honoring Professor Emeritus Kazimierz Malysa from Poland.
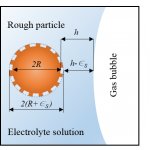
As well discussed in our paper, the interactions of gas bubbles with particles having rough and heterogeneous surfaces are much more complex than the commonly used DLVO – based models predict. The effects of surface roughness on flotation and particle – bubble interactions have been reported many times in the past, although a clear understanding of their origins has been lacking. To explain differences in interactions for spherical hydrophobic particles, a theoretical analysis of the interaction potential was carried out for a model rough particle interacting with a bubble surface in an electrolyte solution in this study. The attractive hydrophobic interaction potential was added to repulsive retarded van der Waals and repulsive electrical double layer interaction potentials. The rough microscopic particles were modeled as spheres decorated with nano-sized asperities. Parameters that reflect common flotation separation systems were selected for testing this theoretical model and computation of the energy barrier applicable to particle – flat bubble surface interactions. It was found that hydrophobic asperities with a height of only several nanometers can reduce the repulsive interaction energy by an order of magnitude. Theoretical analysis also reveals that surface coverage of microscopic particles by nano-sized asperities is important as well.